In this article, we’ll clarify key terms used in indoor planting, ensuring a comprehensive understanding for professionals in the field.
Grow Pot
The grow pot is the original container in which the plant is nurtured at the nursery. It’s the plant’s first home before re-potting or placement.
 The Happy Plant in it’s grow pot
The Happy Plant in it’s grow pot
Decorative Container
Distinct from a grow pot, a decorative container serves both functional and aesthetic purposes. Typically watertight, these containers are essential in indoor settings, often used to house the grow pot itself.
 The Peace Lilly in a Decorative Container
The Peace Lilly in a Decorative Container
Mulch Plate
A crucial component in planter boxes, the mulch plate is designed to support mulch, aiding in moisture retention and aesthetic presentation. Made from materials like metal, plastic, or marine plywood, it’s positioned below the top edge of the planter, with customized holes to accommodate various plant sizes.
 Custom Joinery with a mulch plate for plants and mulch
Custom Joinery with a mulch plate for plants and mulch
Irrigation Systems
Irrigation in indoor settings involves sophisticated systems, often including sprinklers or automated drip lines. These setups require a designated drainage point to manage excess water effectively.
 Irrigation with drip lines
Irrigation with drip lines
Sub Irrigation
An efficient watering method, sub-irrigation stores water underground, releasing it gradually to the plant roots. This passive approach is ideal for consistent moisture delivery with minimal maintenance.
 Sub Irrigation system using water bottle
Sub Irrigation system using water bottle
Direct Planting
This traditional method involves transferring a plant directly from its grow pot into a new pot filled with a suitable growing medium, typically soil.
 Direct Planting
Direct Planting
Indirect Planting
In indirect planting, the plant remains in a grow pot and is placed within a decorative container. This method often requires a mulch plate to support the grow pot.

Watertight
For custom joinery intended to house plants for extended periods, ensuring watertight integrity is crucial. A mere coating of waterproof paint may not suffice; comprehensive waterproofing is essential for longevity using materials such as metal or plastic.
Drainage
Adequate drainage is vital, especially when using irrigation systems. In indoor settings, drainage points should connect to the building’s drainage system, while outdoor settings require strategic placement to direct water away effectively.
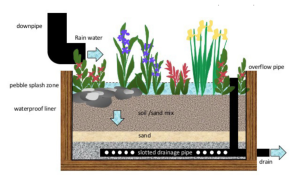
Overflow Protection
Especially pertinent for outdoor containers exposed to rain, overflow mechanisms prevent water accumulation that could harm plants. Without this, containers risk becoming oversaturated, akin to miniature swimming pools.
Filler Tube
Used in both horticulture and irrigation, a filler tube facilitates the watering process, whether filling plant pots or irrigation systems.
 Water is poured into the Filler Tube to water the plant
Water is poured into the Filler Tube to water the plant
Wick System
A wick system employs a porous material to transport water from a reservoir to a plant’s roots. This passive irrigation method is low-maintenance, efficient, and ideal for targeted watering.







